Russia acts as a hacker state. With a full-scale invasion of Ukraine and the continuation of the war, they have already hacked the world security system. International institutions that are supposed to prevent conflicts have not worked.
Now Russia has set its sights on “reassembling” the global monetary and financial system.
The Russians view the introduction of the digital ruble and the consolidation of cannibalistic regimes around themselves to establish horizontal connections between local banks as an opportunity to undermine the SWIFT monopoly and the dominance of the dollar.
The democratic world must give its response to Russia’s next challenge and create a global monetary and financial system free from the defects of the previous one.
***
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said at the G7 meeting in May 2023 that the global financial architecture had become “outdated, dysfunctional and inequitable.” In the face of the fighting in Ukraine and the economic turmoil caused by the pandemic, the system failed to fulfill its function as a “global safety net.”
If after the First World War the central question was who would compensate for the losses caused by the war (the answer was quickly found - Germany), then the Second World War raised the question of ensuring the stability and sustainability of the world economy.
As a result, at the Bretton Woods conference, convened on the basis of the anti-Hitler coalition, in July 1944, the international monetary system of the same name was approved.
The dollar, pegged to gold, replaced the pound sterling as the world's reserve currency. The institutions of the Bretton Woods system (the International Monetary Fund and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development) were created.
And despite the fact that in 1971, with the decoupling of the dollar from gold, the Bretton Woods system collapsed, the “Bretton Woods institutions” - the IMF and the World Bank - continued to exist and personified the liberalization of global markets and financial globalization.
***
In past materials, the authors described the contours of a new global security system, which will be network-centric, multi-level and multi-circuit.
The Russian-Ukrainian war, being not just a local conflict, but a full-fledged world war and a battle for what kind of world this world will be (and whether it will be at all), must resolve another contradiction and create a new global monetary and financial system.
We will try to outline the contours of such a system, which must meet the following criteria:
1. Eliminate crisis factors of the previous system
The collapse of the Bretton Woods currency system (1971) and the decoupling of the dollar from gold actually meant the ability of the United States to issue dollars with virtually no restrictions.
The issue of dollars, tied to the issue of US Treasury bonds, essentially supports consumer demand, primarily in the US economy.
It is believed that under the Jamaican system (which replaced the Bretton Woods system), the number of currency crises especially increased, which began to be double, triple and even full in nature, covering the stock exchange, banking, currency and debt spheres.
In the modern global economy, the main challenge is the reproduction of global imbalances while simultaneously weakening global regulators.
The COVID-19 pandemic has only once again confirmed the ineffectiveness of the neoliberal model of economic growth through increasing the debt burden.
The crisis of the neoliberal model is clearly visible in the graph - from 1980 to 2023, productivity growth continued to accelerate, but wage growth slowed significantly.
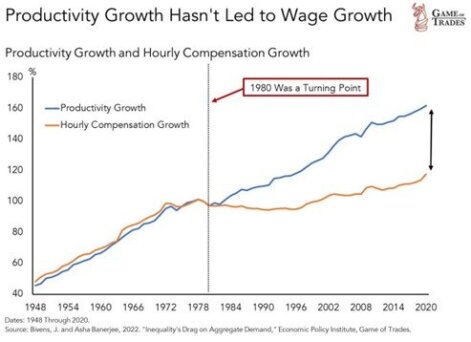
British journalist and publicist Paul Mason in the book “Postcapitalism. A Guide to Our Future notes: “ By the early 1980s, economic growth began to be increasingly supported by debt instruments, causing their total to rise to more than 300% of global GDP by 2010. In the fall of 2021, the size of debt obligations exceeded $300 trillion, and their ratio to global GDP was 350%.
…Capitalism is no longer able to adapt in the way it did during its most successful times in the early 20th century and after World War II. It no longer allows value to be created from skills and performance.”
That is, we are seeing the exhaustion of the potential for industrial growth and the inability of the service sector to create wealth - it can only be created from credit money.
In turn, the ability to consume goods and services is a finite value, and accelerated credit (especially at near-zero rates) and emission (not backed by goods) stimulation provokes hyperinflation.
What else Mason noted is that “ the digital economy in the current structure of “classical” capitalism has contributed to an unprecedented concentration of wealth . ”
That is, on the one hand, there is excessive accumulation of financial capital, on the other, the impossibility of endless expansion of markets, as a result of which the efficiency of capital is constantly decreasing.
And attempts to further stimulate consumption with credit lead to a debt crisis, precisely due to the low efficiency of capital.
An attempt to revive the neoliberal model was presented by US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen as the “New Supply-Wide Economics”.
Classic supply-side theory uses tools such as aggressive deregulation and tax cuts to promote private investment to increase potential output.
Janet Yellen argues that "old supply-side economics" failed by failing to accelerate economic growth.
The modern “ supply -side economy ” can be reduced to a simple idea : what is needed is not a high growth rate per se, but growth that is based on inclusiveness and the principles of green sustainable development.
“New supply-side economics” implies:
- investments in human capital at all stages of education: from kindergarten to high school and vocational guidance;
- investments in infrastructure (both new types - broadband Internet, and traditional ones - ports, roads and railways);
- new rules for taxation of multinational capital (essentially deoffshorization).
At the same time, despite deregulation, there is an attempt to implement greater regulation of the economy by the state through active investments in education, science and innovation.
Despite the fact that the “new supply-side economy” is still within the framework of the neoliberal model and capitalist system, the drift towards greater government intervention is obvious.
In response to global challenges, the transformation of the US economy is taking place along two main tracks: reindustrialization and the transfer of vital production to US territory.
The federal government invests directly and creates interconnected incentives and at the same time restrictions on businesses to create secure supply chains that are impossible under the free market.
The choice for more regulation will also be determined by:
- the desire to avoid a financial and debt crisis;
- development of technologies that allow more efficient organization of management processes;
- the desire and technical ability to solve the basic contradiction of the capitalist system and its main vulnerability, which the “new supply economy” is not able to solve.
***
The interest rate on which the market economy is built is also its basic contradiction, which leads to a cyclical debt crisis.
Back in January 2023, the United States hit the national debt ceiling and came close to the first default in its history (although the collapse of the Bretton Woods currency system de facto led to a default).
“A default on our debts would lead to economic and financial disaster,” Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen warned.
The maximum amount of national debt is limited by law, and despite the fact that the revision of the ceiling became the subject of political bargaining , a compromise was reached in Congress and a default was avoided.
Congress approved a compromise and allowed the US national debt to increase above the already reached record 31.4 trillion dollars. Currently, the US national debt is 35 trillion. dollars and continues to grow every second.
The rule on the maximum size of the national debt will cease to apply on January 1, 2025, which means that in less than six months the question of the risk of US default will arise again.
It is impossible to resolve this contradiction while remaining within the market paradigm.
Therefore, considering the danger of a financial catastrophe on a planetary scale, most likely, this problem will be solved in a way that is no longer entirely market-based.
2. Ensure the economic superiority of the Western cluster, stimulate its development and greater competitiveness
In previous works, the authors outlined the economic aspect of global changes - the upper level of international trade will be represented by macro-regional clusters:
- conditionally Western or Euro-Atlantic (including the countries of the Pacific region belonging to the conditional Western camp);
- Chinese – trying (most likely hopelessly) to catch up with the Western cluster;
- “Non-Aligned Movement” , the flagship of which will be India, which will still gravitate towards the West.
- Despotic - a cluster of world outcasts (Russia, Belarus, Iran, North Korea, Syria, etc.), which will act as a Chinese proxy.
Under the rules of the World Trade Organization (another institution created after World War II), China completely crushed the United States and Europe.
That is why the WTO is in a deep crisis, which is most likely man-made.
The WTO has also failed to lead the world to global trade agreements.
According to the World Bank, the share of global trade in goods and services in global GDP as of 2022 was 31.1%, which is the same as in 2005.
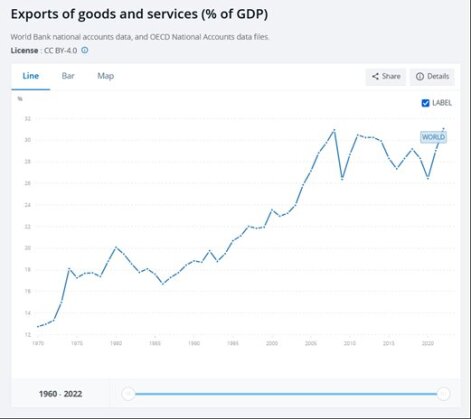
Against the backdrop of the ongoing Russian-Ukrainian war and Houthi terrorist attacks in the Gulf of Aden, we can hardly expect an increase in global trade.
Ultra-globalization has essentially stopped, and in the New World globalization will be of a cluster nature.
WTO chief Ngozi Okonjo-Iyewala is already seeing signs of states dividing into blocs, such as the fragmentation of the semiconductor market.
Due to fragmentation of trade and division into blocs, in her opinion, the global economy could lose up to 5% of GDP in the long term.
The Western macrocluster is rapidly moving into the sixth technological structure, which will be a hybrid of information and production technologies.
***
Consonant with the “New Supply Economy” from US Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen is a document called “Industry 5.0. A transformational vision for Europe. Managing Systemic Transformations towards a Sustainable Industry” , issued in 2022.
According to the authors of the document, industry must take into account aspects that were not taken into account in Industry 4.0:
- regenerativeness of industrial transformation;
- social dimension;
- environmental aspect.
Industry 5.0 is not a technological leap, but a direction of technological transformation of industrial production for the prosperity of people, the planet, etc.
At the 2021 summit, G7 leaders announced the need to change the neoliberal paradigm known as the Washington Consensus, and that economic success should be measured not by GDP growth figures, but by the degree to which the overall UN sustainable development goals are achieved. Which implies large-scale implementation of carbon-neutral energy production.
At the same meeting, G7 leaders committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, cutting emissions in half by 2030, and protecting at least 30% of land and oceans by 2030.
Thus, the Western macrocluster, through the “green transition,” plans to ensure a higher technological level of its economy by levying a carbon tax on goods produced outside the cluster using cheaper “dirty” energy.
G7 members also reportedly intend to limit China's influence on global trade and end practices that "undermine the fair and transparent functioning of the global economy."
At the same time, the leaders called on the Chinese leadership to respect human rights, especially with regard to the ethnic Muslim minority of the Uyghurs.
The current format of free trade is completely devoid of an ethical component. And the world hegemon has to manually resort to economic sanctions, wasting its reputational capital.
In the New World, the cluster type of globalization will make it possible to apply any tariff and non-tariff methods (including openly discriminatory ones) against other clusters that do not share the values of the Western macrocluster, be it the use of “dirty energy” in the production chain, forced labor or violation of the rights of small nations.
3. Be network-centric, but maintain the leadership and guiding role of the United States
William Burns, director of the CIA, in his article for Foreign Affairs, “Espionage and Statecraft,” essentially formulated a rethinking of the role of the United States in the new world.
He applied it to the Middle East, but it can be extrapolated to the whole world.
“The United States does not have the sole responsibility for solving any complex problems [in the Middle East]. But none of them can be advanced, much less resolved, without active US leadership.”
The dollar, as the world's reserve currency, is responsible for the global economy. And in the New World, the United States does not want to bear this exclusive responsibility.
The constant issue of dollars made sense in the form of stimulating economic growth, albeit at the cost of increasing public debt. And the need for the presence of the United States in all world affairs was intended to protect the hegemony of the dollar as a reserve currency.
Based on the understanding of the new format of the world economy, the new monetary and financial system will not assume the presence of a global reserve currency.
Therefore, the US attempt to reset the monetary and financial system will be undertaken in such a way that, in addition to eliminating crisis-producing factors, it will maintain control over it.
This can be done by creating (primarily by the States and possibly the UK as a leader in global fintech) a new model of global cooperation in the field of sustainable finance and regulation of financial services, as well as offering a technical platform on the basis of which this model will operate.
to be continued
Authors:
Vladimir Shevchenko , political scientist, Doctor of Philosophy
Andrey Savarets , analyst, lawyer, author of telegrams for the “ Minority Opinion ”

























